Electronic design projects usually use a group of software tools in the design of electronic systems including integrated circuits, printed circuit boards and electronic products from appliances to weapons. Suffice it to say that the technology is a crucial component of the manufacturing process across diverse industries.
But not every company has the capability in technologies, manpower and resources to undertake projects on their own, thus, the necessity for outsourcing. In itself, outsourcing has several benefits including tapping into the proven technologies, manpower and networks of the third-party provider and enjoying the desired results, which translates to excellent value for the money. Then again, outsourcing has many pitfalls wherein anything and everything can go wrong – and in sensitive projects involving electronic design, something going wrong can quickly become a nightmare.
The benefits of outsourcing design projects will then partly be determined by the quality (i.e., experience and expertise, reliability and reputation) of the engineering firm hired for the purpose and partly by the quality of coordination each party has with the other. Start asking for references for the best engineering firms in the industry and then make your choice from the shortlist after careful consideration of their suitability for the project.
Companies offering electronic design projects for outsourcing should be aware of three dangers in the process. First, the lack of familiarity between the two parties specifically in their operations will hinder the design process in so many ways – the right results may not be delivered in the right time to the right person, for example. Your company may not be familiar with the engineering firm’s processes in design projects and vice versa.
Second, the lack of preparation on the part of the company outsourcing the design work will jeopardize the entire project, too. Keep in mind that the company must have a project plan including detailed functional specifications before the project can be handed over, so to speak, to the contractor. Otherwise, mistakes will abound and reworks will be necessary, which will add to the overall costs – truly, something that any company will want to avoid.
Third, the lack of a written agreement (i.e. formal contract) can result in several disagreements, if not lawsuits. Intellectual property rights (i.e., who owns what part of the project) are thorny issues that every company outsourcing its electronic design projects must be aware of.
When any of these things manifest themselves, both the company and the contractor will have to deal with a wide range of issues. Think of incorrect results, inappropriate specs, and innumerable reworks, which are relatively mild in comparison with stolen design ideas, industry espionage, and violations of intellectual property rights.
Fortunately, these are issues that can be avoided with careful planning even before the electronic design project is outsourced. Do your homework on the specs for the project and the contractor for it. Work with the contractor on every aspect of the project so that mistakes can be detected and resolved early on. Get the terms and provisions of the project in writing.




 It’s likely that you’re working much more with digital equipment these days, but the fact remains that without good old fashioned mechanical design, our lives would be vastly different – and much more inconvenient – than they are.
It’s likely that you’re working much more with digital equipment these days, but the fact remains that without good old fashioned mechanical design, our lives would be vastly different – and much more inconvenient – than they are.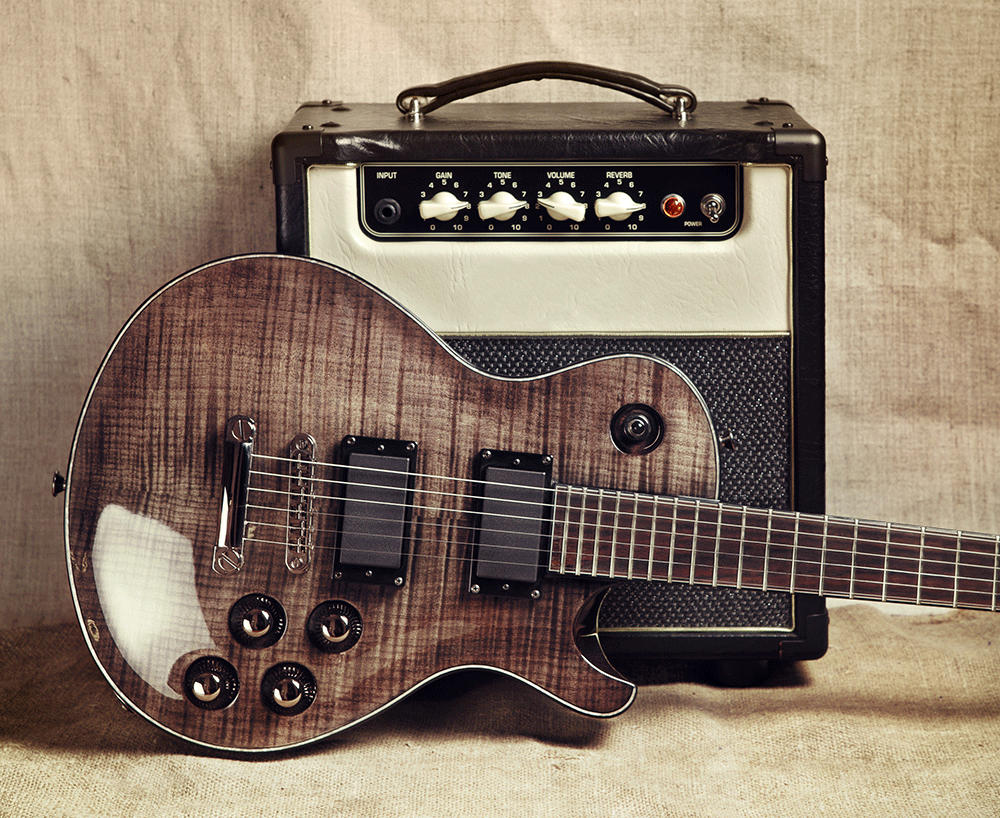
 The strange thing is that it’s not just rock guitar amps which use valve technology. Every professional recording studio will use valves in their production hardware – even computer based genres like house, trance and sample-driven hip-hop. This is because specialist music production hardware such as compressors (which reduce the dynamic between loud and quiet signals) and graphic EQs (which boost some frequencies and reduce others) simply sound better when valves are introduced. Something about this inefficient – and, by now, archaic – technology appeals to the human ear that modern transistors, ICs and software doesn’t. There’s no scientific reason why this is the case, but industry experts and casual listeners all seem to agree – a vacuum tube is the best sounding form of amplification there is.
The strange thing is that it’s not just rock guitar amps which use valve technology. Every professional recording studio will use valves in their production hardware – even computer based genres like house, trance and sample-driven hip-hop. This is because specialist music production hardware such as compressors (which reduce the dynamic between loud and quiet signals) and graphic EQs (which boost some frequencies and reduce others) simply sound better when valves are introduced. Something about this inefficient – and, by now, archaic – technology appeals to the human ear that modern transistors, ICs and software doesn’t. There’s no scientific reason why this is the case, but industry experts and casual listeners all seem to agree – a vacuum tube is the best sounding form of amplification there is.
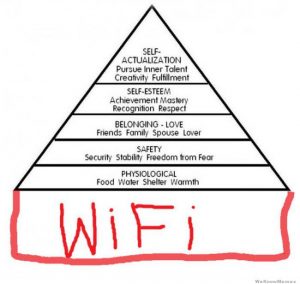 This image shows how most people see their human needs according to Maslow’s scale. It is of course mean as a joke, but it does point out how important WiFi is to our society. Electronic design behind a range of boosters, amplifiers and extenders means that you can browse quicker and further from your wireless router thanks to the following factors:
This image shows how most people see their human needs according to Maslow’s scale. It is of course mean as a joke, but it does point out how important WiFi is to our society. Electronic design behind a range of boosters, amplifiers and extenders means that you can browse quicker and further from your wireless router thanks to the following factors:
 A new electrical product can have everything going for it – strong marketing, little direct competition, and a good visibility campaign, but if its electronic design isn’t absolutely perfect, then the product could be victim to faults, unnecessarily expensive components, or heat and power problems which can cause a product to fail.
A new electrical product can have everything going for it – strong marketing, little direct competition, and a good visibility campaign, but if its electronic design isn’t absolutely perfect, then the product could be victim to faults, unnecessarily expensive components, or heat and power problems which can cause a product to fail. 
 The old product design adage is that “if companies spent as much on their products as they did on advertising, they wouldn’t need to advertise”. This couldn’t be further from the truth. Without Apple’s masterful marketing campaigns it wouldn’t be able to even attempt market dominance against Google, Samsung and Amazon. However, by using masterfully selected product placement in TV, movies and music videos, as well as minimalist, humanist advertising, inspired in no small part by founder Steve Job’s famous “reality distortion field” – a mix of laser-like business acumen and Jedi mind trickery – Apple has established itself as a true market leader, able to command retail prices in excess of 150% of its closest competitor.
The old product design adage is that “if companies spent as much on their products as they did on advertising, they wouldn’t need to advertise”. This couldn’t be further from the truth. Without Apple’s masterful marketing campaigns it wouldn’t be able to even attempt market dominance against Google, Samsung and Amazon. However, by using masterfully selected product placement in TV, movies and music videos, as well as minimalist, humanist advertising, inspired in no small part by founder Steve Job’s famous “reality distortion field” – a mix of laser-like business acumen and Jedi mind trickery – Apple has established itself as a true market leader, able to command retail prices in excess of 150% of its closest competitor.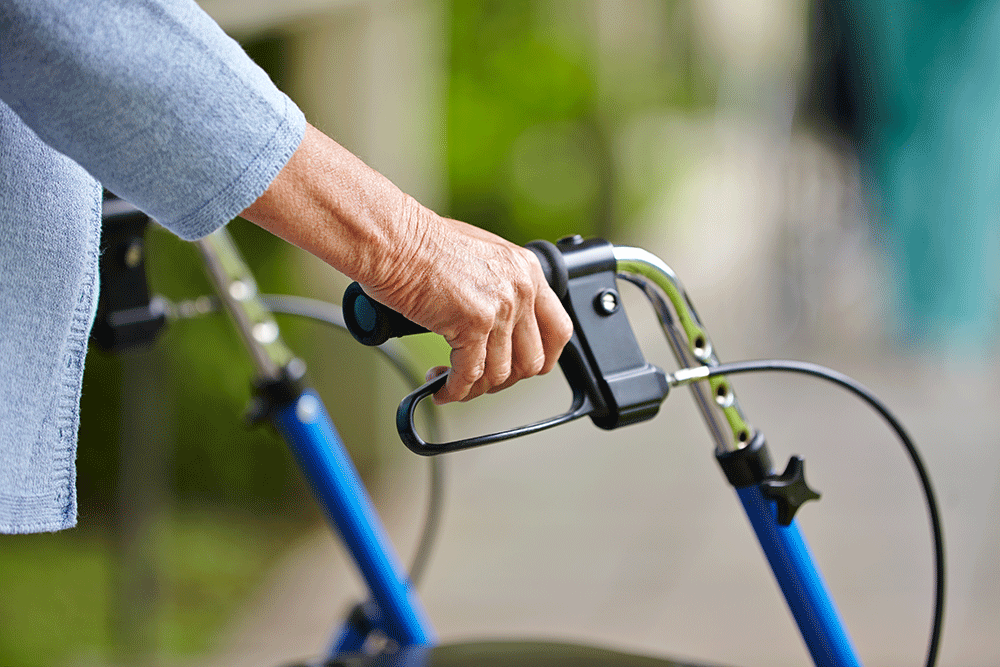
 These products are often very simple, serving a specific purpose. The prime example is the Helping Hand – a simple extending grabber which allows people in wheelchairs to reach and carefully move items around their home and work. There couldn’t be a simpler concept – squeeze the trigger and two prongs move together – but there are quite specific design points to consider in order to make sure the end users’ needs are fully satisfied. Materials used, resistance in the mechanism, and extra features like extendability all need considering as they could mean the difference between a product dominating the target market, or making a financial loss.
These products are often very simple, serving a specific purpose. The prime example is the Helping Hand – a simple extending grabber which allows people in wheelchairs to reach and carefully move items around their home and work. There couldn’t be a simpler concept – squeeze the trigger and two prongs move together – but there are quite specific design points to consider in order to make sure the end users’ needs are fully satisfied. Materials used, resistance in the mechanism, and extra features like extendability all need considering as they could mean the difference between a product dominating the target market, or making a financial loss.
 Apple’s product design and marketing have become textbook examples of how companies need to operate. Their marketing plans have become tech startup companies’ Bibles, and Steve Jobs has passed into business legend. But how did they do it?
Apple’s product design and marketing have become textbook examples of how companies need to operate. Their marketing plans have become tech startup companies’ Bibles, and Steve Jobs has passed into business legend. But how did they do it?